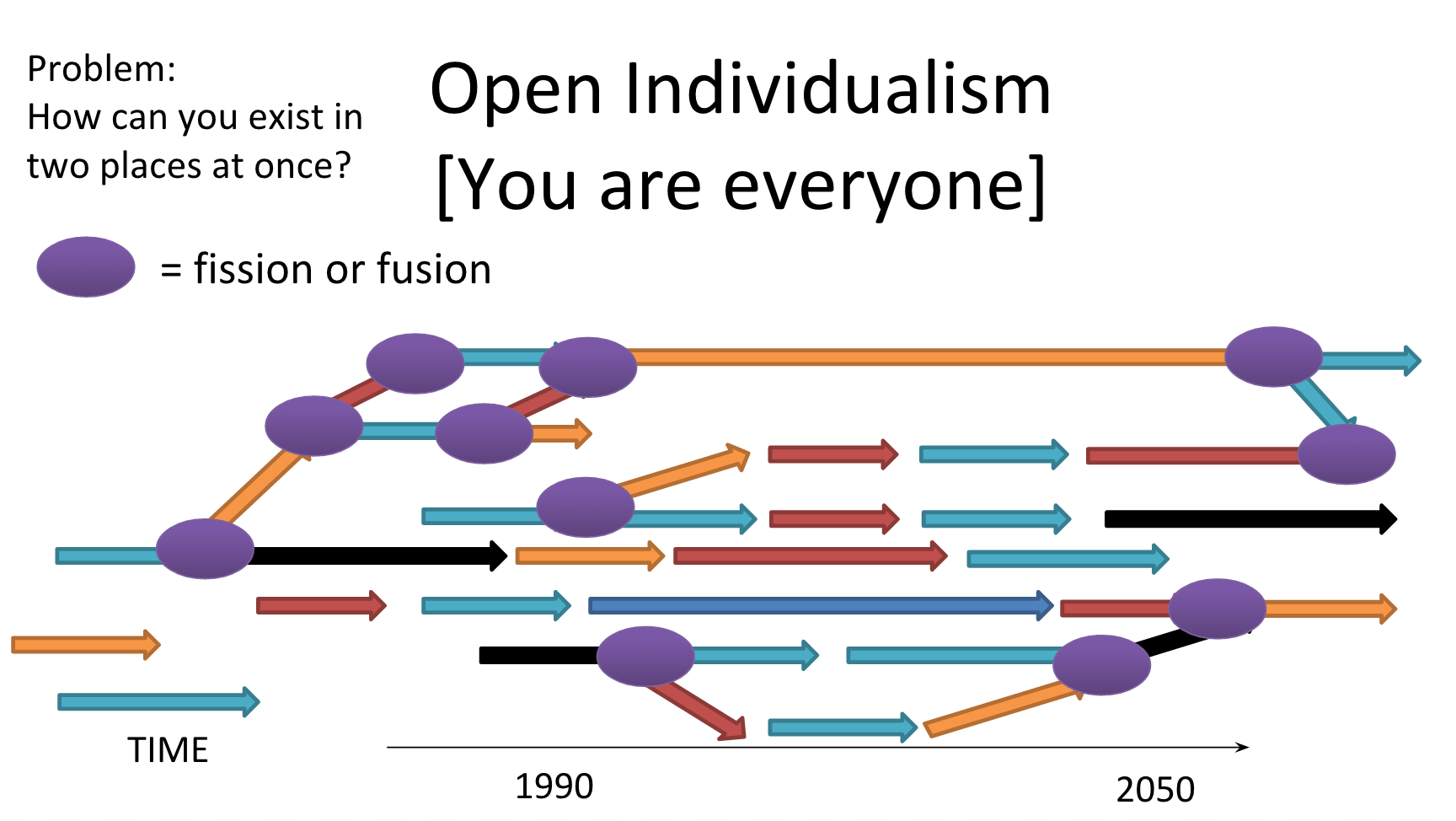
The following is an exchange of text messages with Roger Thisdell, a 26 year old accomplished meditator. He claims that this year he finally broke through into abiding in what he describes as an entirely new category of experience that matches the descriptions of classical Buddhist 4th path.
For context, Daniel Ingram of Mastering the Core Teachings of the Buddha fame describes 4th path as:
1) Utter centerlessness: no watcher, no sense of a watcher, no subtle watcher, no possibility of a watcher. This is immediately obvious just as color is to a man with good eyesight as the old saying goes. Thus, anything and everything simply and obviously manifests just where they are. No phenomena observe any others and never did or could.
2) Utter agencylessness: meaning no agency, no sense of doing, no sense of doer, no sense that there could be any agent or doer, no way to find anything that seems to be in control at all. Whatever effort or intent or anything like that that arises does so naturally, causally, inevitably, as it always actually did. This is immediately obvious, though not always the forefront of attention.
3) No cycles change or stages or states or anything else like that do anything to this direct comprehension of simple truths at all.
4) There is no deepening in it to do. The understanding stands on its own and holds up over cycles, moods, years, etc and doesn’t change at all. I have nothing to add to my initial assessment of it from 9 years ago.
5) There is nothing subtle about it: anything and everything that arises exhibits these same qualities directly, clearly. When I was on the third path, particularly late in it, those things that didn’t exhibit these qualities were exceedingly subtle, and trying to find the gaps in the thing was exceedingly difficult and took years and many cycles. I had periods from weeks to months where it felt done and then some subtle exception would show up and I would realize I was wrong yet again, so this is natural and understandable, and if someone claims 4th as I define it here and later says they got it wrong, have sympathy for them, as this territory is not easy and can easily fool people, as it did me many, many times over about 5 years or so. However, 4th, as I term it, ended that and 9 years later that same thing holds, which is a very long time in this business.
There are other aspects that may be of value to discuss at some other time, but those are a great place to start for those who wish to claim this. If you truly have those, then perhaps we can talk about a few other points that are less central and essential.
[Links added to aid reader’s comprehension – lightly edited for clarity]
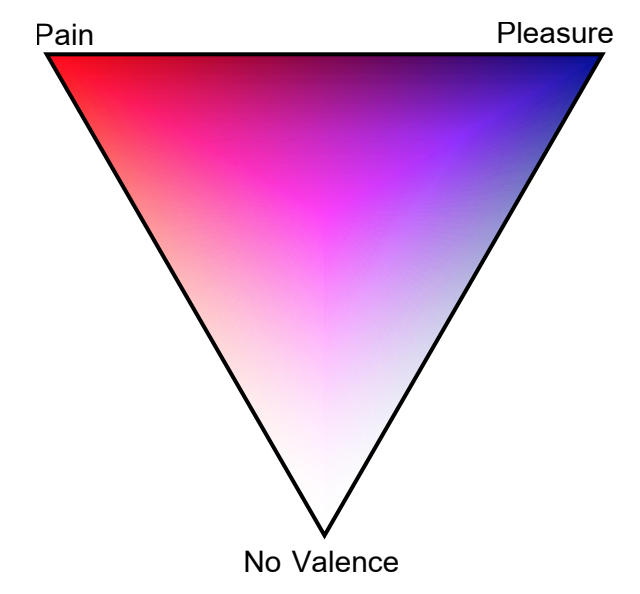
In the beginning… Roger joined a private group where we discuss consciousness and started to get familiar with the vocabulary of the Qualia Research Institute (e.g. discussing meditation in terms of valence). He then posted this video, which caught my attention:
Where he claims that “Pleasure as a positive, as an actual added experience, does not exist. It certainly does not exist how a lot of us think it does … [whereas] negative valence experiences do exist as contractions.”
Based on that very interesting video, I decided to invite him to Phenomenology Club (a private gathering where we discuss exotic states of consciousness and try to make sense of them in a think-tank fashion – see Healing Trauma with Neural Annealing).
Conversation
Roger:
Andrés! This is Roger Thisdell […]. Thanks for giving me your number.
Do add me to the Phenomenology Club. That sounds like my jam! Cheers!
Andrés:
Excellent! Will do! 🙂
[…time…]
Roger:
Hey Andrés, it was great to hang out online last night and hear your explanations. A bunch of you are really elite thinkers. I’m inspired to learn how to speak more of your qualia language.
I would love to get into the topic of paradises with you. You seem to really sing their praise.
I said yesterday that I hold the view that actually what is most desirable is just the elimination of negative valence. As someone who frequently has cessations (when consciousness blanks out for a moment) where there is no subjective experience (no negative, no positive valence) in my book this is good enough. My thinking is also informed via complete ego death experiences in which there is still consciousness but no judgement on any part of experience (bad or good). At a local individual level these are the most desirable states. Out of all the states I have experienced (including bliss trips, jhanas, 5-MeO, MDMA, staring into the eyes of a lover without insecurities, laughing fits 🤣) if I had to choose a state to be in permanently it would either be cessation or ego death. I may have curated my brain too much to a Buddhist view and my level of emptiness insight is well entrenched, so that it is hard for me to really believe the ultimate good is to keep the cosmic consciousness party going and fueling it with positive valence.
I think that while consciousness is online we better make the best out of it and try to exist in as few low negative valence states as possible and help all sentient beings with this as well; all the while the positive valence that comes along is merely instrumentally valuable, like a compliment or added bonus.
For example if you are hungry it is nice to eat something tasty. But if you were never hungry in the first place then who cares how tasty something is – don’t need it 💁♂️ (this may be my strongly consolidated non-attachment showing).
I guess what I’m really asking is: can you convince me to intrinsically care for paradise states? I do believe I have experienced what you are referring to as paradise states, but maybe I just have too much non-attachment for them to think they are the goal/prize.
(apologies for being long-winded 🙏)
Andrés:
Perhaps:
- You lost the ability to get excited about future experiences. You learned this because you were taught and you practiced techniques that associate being excited about the future with dukkha. Alas, the hedonic theories around the time of Buddha were incomplete and as a consequence a lot of the claims and teachings underfit reality (meaning that they generalize too much). In contrast, it turns out that there are a manifold of ways of experiencing excitement about the future in an epistemologically clear way and no delusions. More so, with that orientation one can see more clearly larger parts of the state-space of consciousness as one is not inhibiting them. I know you have experience with high valence states. But I suspect you have deconstructed a lot of the microcognitive apparatus that allow the insights coming from the reality of their existence from propagating across the entire nervous system.
- Just as lack of awareness about e.g. cluster headaches phenomenology can give you the impression that reality has no stakes, so does acute lack of access to the ultra-positive realms. I think for many, Buddhism has a certain effect in how one conceptualizes such experiential realms after the fact that perhaps is not quite in tune with how they truly were. Interestingly, one could here examine Buddhism as an aesthetic itself, and renunciation as a kind of Soulmaking, where under the hood one is still pursuing a kind of high-dimensional meaning qualia of positive valence. Which takes me to:
- Rob Burbea’s Soulmaking talking about how exploring not exhaustively breaking down dukkha always but letting a bit of e.g. Eros/passion for reality opens up new ways of seeing that recontextualize Buddhism. Not that we shouldn’t get rid of dukkha, of course. But it’s good to see the underlying aesthetic influences on how one generalizes about reality based on one’s experience.
What do you think? 😄
Thank you for joining! And also for sharing your thoughts. 🤠👌
See: Soulmaking part 1, part 2.
Roger:
Ah Andrés, so many thoughts 🙈
First of all, I am so impressed with Burbea. His lectures were incredibly useful for me while learning the jhanas. And now I’m picking through his book ‘Seeing That Frees’.
I think his ontology and how he builds on Buddhism is sophisticated and gorgeous.
Reminds me of a remark about Hemingway, by his grandson – he quit journalism to dedicate himself to fiction because he was more interested in truth than facts. I relate this to Soulmaking in a way.
I love his notion of skillful fabrication. But it seems like it’s a compromise in a way. We can’t fully live without self, and thoughtforms, and conceptual frameworks, and so, while we are alive and have them, let’s learn to use them skillfully/beautifully. I’m on board! 🚂
Re your 2nd point: I would add that a lack of awareness of the existence of cessations, or Nirodha, or ego death experiences is another topographical blind spot which prevents people from making a more comprehensive assessment of what is most desirable. (I know that many people who say they’ve experienced ego death, when I enquire about it, it turns out to be more of just a partial ego loss experience, and not the full annihilation). I suppose we really need those who have deep expertise in bliss states and dukkha-less/unfabricated states to compare and contrast.
For what it’s worth, and to give you more a sense of my bias, I would claim to be someone who has explored a wide range of state-spaces: from suicidal depression, to psychosis-like damnation bad trips, to K-holes, to peak experiences, and now as of 21st of May [2021] I’m claiming Frank Yang-style MCTB [see: Scott Alexander’s book review] 4th path permanent abiding in centreless consciousness (IDK what that says about my nervous system and fully propagating insights as you mentioned).
Hands down 🙌, this is the best shift in my life that has ever taken place without a doubt (I thought stream entry was good, but this is another magnitude). My hedonic set tone is persistently so high. I’m often walking around smiling for no apparent reason. 11/10 I recommend this.
And 4th path gets you an ability to adopt a new perspective where you simultaneously see the Yin and the Yang and vice sera (emptiness is form and samsara is nirvana). It’s all one place, there is not out. All the while, still we quite obviously make value judgements between states. I know you speak of hellish corners of consciousness that shouldn’t be touched. And so, although we can/should adopt flexibility of perspectives on aesthetic frames (as Rob speaks about, which is helpful) and see value in many different views as best as we can… must we still do the hard job of really judging what is best? What is most desirable? (to talk from a metamodern perspective).
Ultimately, I still come down on: lights out unconsciousness tops everything 🤷♂️ [emphasis mine]. Getting all beings to Parinirvana would objectively be preferable for all beings rather than keeping the play going – if such a plan is possible or sensible or sensical even.
It’s funny though, at some point I think it may just come down to some split difference in intuition among people (perhaps that difference can be reconciled somehow). For me this was apparent when I hear from Kenneth Folk vs. Culadasa. Kenneth holds antinatalist sentiments (or he did when I emailed him a couple of years ago and actually asked him) which speaks to a siding with a belief that there is an asymmetry of weighted value between negative and positive valence. While Culadasa seems to emphasize the joyous journey and adventure of life, which may speak to an opposite weighting in favor of the positive valence being worth the negative valence that comes along with it. Certainly not all spiritual roads lead to Rome.
I am very open to the idea that I am missing something though, and I may just need to be led by the hand like a child to these heaven realms for me to change perspective 😇😂
Thanks for engaging, this is fun!
Andrés:
Thank you for engaging! This is super interesting! Let me think about what else I can say 🙂
[…time…]
Total valence vs. pureness of valence: see Principia Qualia pg. 41. It could be that during cessations consciousness disappears and the state literally does not exist in any way. But the states immediately before and immediately after do and have at least a tiny bit of information so they are mixed valence states. Yet, perhaps they are massively positive valence on net.
An alternative view is that unconsciousness is still ‘real’ in a way, in which case we could think of it as consciousness but with no content whatsoever. But it’s still there. The analogy would be like combing a vector field in a torus. Most states have the vector field collide with itself and therefore feel less than perfect valence (due to [the Symmetry Theory of Valence, aka.] STV). Only when the field is completely combed without any self-collisions (which would not be possible in a sphere) you get perfect positive valence. And although there is no information encoded in the field, it still exists just as it did before. There’s just nothing to report.
In that case paradise could actually still exist. Meaning, higher and more refined versions of this kind of experience. In particular, we could look for other mathematical objects where the field can also be combed perfectly. They would then be strangely a different kind of ‘unconsciousness’ perhaps capable of fitting more energy and higher dimensions. Still, they would have maximum positive valence.
What do you think?
Oh, I also forgot if I’ve asked you whether you’ve tried 5-MeO-DMT and how it compares to your new baseline.
Images from Michael E. Johnson’s Principia Qualia
Roger:
Ah, yes, I see the kind of framework you’re thinking from now – anti-symmetry, symmetry, and asymmetry.
From Principia Qualia pg. 39: [paraphrasing] “…if we take our hypothesis and apply it to IIT, and then we attempt to maximize pleasure/symmetry, consciousness/[phi] drops very rapidly.”
All the way to the point that maximum pleasure entails no consciousness??? [emphasis mine]
I don’t have a lot of experience with 5-MeO. I only did it once at about a 6mg range.
My impression of 5-MeO was that it had a visual brightening effect somewhat similar to the 4th Jhana. And there was that psychedelic mirroring effect with eyes open. It also had the reduction of conceptual understanding that comes when you get into 8th [Jhana]. I interpret that as a significant down-regulation in top-down information processing??
5-MeO has the sense that it’s going somewhere, moving towards something, while the effects build and then dissipate. Like it’s growing into something (I guess this is before a peak breakthrough – which I didn’t have).
My current consciousness abode isn’t going anywhere. There isn’t a sense that things are building towards something. It has a forever ‘this is it’, locked-in quality. Like a somewhat superposition of emptiness and fullness simultaneously. (Before 4th path I always felt like I was flickering between form and emptiness, now the two cohabitate the experiential space at the same time).
5-MeO also seemed very hedonically volatile; like any subtle thought or movement could disrupt the peace.
Meanwhile my current state is super unperturbable. In the past 2.5 months I haven’t found something that has rocked my well-being.
A couple of weeks ago I listened to an interview of a North Korean defector tell her story of starvation and human trafficking and for a good 30 minutes I was crying at this tragedy. But it was crying from a place of still really high well-being. I didn’t feel like I was suffering and I didn’t mind that crying state at all. (Which is quite weird, I suppose).
In my normal state now, there are no more papañca attacks. Thoughts don’t capture the mind like they used to.
And another thing I love about this new state is that I still have all my cognitive functions intact and I can operate in the world totally normally – which can’t be said about being on 5-MeO.
I feel super sober; while on 5-MeO I don’t believe you do (if I remember correctly).
I would say I prefer my new baseline to what I experienced on 5-MeO because of the lack of volatility and practicality of still having my intellect on hand, all the while with the constant sense of ‘this is it’ and high, high well-being.
[…time…]
Roger and Andrés have a video call:
We discussed a number of things: his meditation journey, his thoughts on various philosophies, exploring QRI frameworks, and his interest in music. Curiously, Roger said that unlike other people who spend a lot of time in meditation healing traumas and processing past experiences, he was able to largely just focus on progress on the path. This, along with a very rigorous and consistent practice, is why he got to where he is at so early in life (26 years old).
One of my main interests in the discussion was to flesh out how 4th path states/traits and the Symmetry Theory of Valence (STV) were connected. If I recall correctly, there were three main ideas connected to this topic I shared with him:
- Discussing the “levels of consciousness” experienced on a psilocybin trip and the way they might mirror some of Frank Yang’s descriptions of the levels of consciousness on the path to awakening,
- A model of equanimity I’ve been developing where impedance matching is a key ingredient, and
- The difference between a “recipe” of a state or transformation of consciousness and its “review”
Let’s briefly elaborate on these topics.
(1) Frank Yang talks about undergoing a meditative process with the following stages: (a) standard sense of self, (b) awareness of awareness, (c) God/Oneness/Being/Non-Duality/Self, (d) Emptiness/Non-Beng/Uni-Locality, (e) Neither Being Nor Non-Being, and finally (f) Enlightenment.
(source)
What makes his descriptions so incredible is that he provides very raw and unfiltered phenomenological accounts of the process without really trying to force them into any pre-existing framework. From the point of view of the mission of QRI this is very valuable. In particular, it allows us to examine his process of transformation with the framework of Qualia Formalism: we ought to ask, not what kind of spiritual/mystical/transcendent process is going on here (which will certainly take us nowhere), but rather, wonder if we can cast his descriptions in terms of *structural changes to the field of awareness*. For example, Frank talks about “the screen of God” that becomes apparent in (c), where waves of energy seem to travel without resistance across one’s experiential field. He also talks about phase transitions (similarly to Shinzen Young, he talks about a process of liquefaction and gasification of the field of awareness). If, as we believe at QRI, valence is a structural property of experience, these transformations would have profound effects on one’s sense of wellbeing. So, the reason why “the screen of God” is a profound experience is not because you literally merge with a divine being (which might not be possible if we assume indirect realism about perception), but because the field of awareness is now in a phase that allows an entirely new level of efficient stress dissipation.
I shared with Roger some details from a particularly interesting psilocybin trip report that described rapid phase transitions between (what appears to be) several of the levels Frank describes. In particular, “the screen of God” state seems to have the capacity to stresslessly locate sensations without generating reverbarions with a represented “small self to which those sensations belong”.
(2) In turn, this led to discussing a new model (we haven’t really touched upon in QRI publications yet, but which is coming) of equanimity based on experiences I had during a two-week retreat earlier this year (see: Buddhist Annealing). This model has at its core the idea that equanimity is a mental tool that increases impedance matching between nervous system harmonics. Ask yourself: why is it that when you pluck a guitar string it sounds louder if it is connected to a guitar? It is not, as many would think, that the “resonance box amplifies the sound” (for where would the extra energy come from?). Rather, the energy is the same; what changes is the speed at which it is discharged! The resonance box vibrates and dissipates the energy of the string much faster than the string could on its own (as an aside, this is exactly why you can sustain a note for so much longer in an electric guitar). We could thus postulate that a lot of inner dissonance comes from resonance in the nervous system that has no means of dissipating its stored stress. To an extent, this is because involuntary subliminal contractions in our nervous system compartmentalize and modularize its components. Equanimity is the practice of relaxing those contractions, and thus slowly allowing the nervous system to undergo a search process where it finds structures that can resonate with the stored stress, and in turn allow it to dissipate faster. More so, over time, you entrain (and rewire!) the nervous system to become highly efficient at stress-dissipation. Dissonance is still there, but it “unfolds” and gets “metabolized” so fast that it barely counts as suffering. Highly annealed nervous systems are powerful stress-dissipation engines!
(3) Finally, we also discussed the idea that there is a distinction between the “recipe” of a state of consciousness and its “review”. A recipe is the steps you take in order to achieve a certain state (or transformation) of consciousness. A review is instead an account of what the resulting state feels like. Just as the instructions for baking a cake are quite different from a Chef’s review of what the resulting cake tastes like, we can expect that meditation instructions (e.g. focusing on the three characteristics) will not necessarily reflect the nature of the transformations of consciousness that result from them. Thus, while a lot of the meditative path is nominally about “renouncing” the pursuit of high-valence states of consciousness (and thus avoid the pleasure paradox), the result is nonetheless a state of consciousness that is high-valence in nature! Paradoxical? I don’t think so. The confusion is merely the result of conflating recipe and review.
Thus, we can still apply valence theories to states of consciousness that are allegedly beyond valence. Frank Yang, for example, seems to resonate a lot with STV. See his December 2020 interview at The Stoa. There (and in other videos) he describes “God mind” consciousness as a very positive experience, which is very symmetrical but not perfect. But his true awakening is perfectly symmetrical (in the realm of space, observer, and sense of time, even if not in content). His experience became like a “hologram that has no center”. Quote:
“Have you seen those illustrations of a sphere or a circle, where one point connects to all of the other points? […] if you wanted me to describe my day to day, moment to moment, experience, well, it’s pretty symmetrical. As in, there is no center to experience. There is hearing but no hearer; there is just the seeing, there is no seer; on thinking there is just thinking and no thinker. It’s not, like, processed or filtered through a subject in the center. And it’s very immediate in the sense that all of the sensations, all 360 degrees, are synched up to themselves, without any delay, 24/7. And all the sensations, where there is body, you know sight, sound, thoughts, emotions… they are all on equal footing to each other […inaudible…] in symmetry, and that is for me an aesthetic experience. I would say a suffering mind is a mind that isn’t symmetrical. If your mind is asymmetrical, it means it’s defiled somewhere. So for me aesthetics runs in all different kinds of domains, not only on the perceptual domain, not only on the visual aesthetics domain, but even on the emotional and how you think.”
Yes, God Mind (left) is good, but have you tried no-self (right)? It is so much more symmetrical!
As we’ve discussed before, the homogeneity of phenomenal space and time might be a very large component of what accounts for positive valence. And what Frank is describing here suggests that’s the case. Disturbances in the attention field lines and the saliency of specific components of a mind can break the underlying symmetry of the phenomenal space and time of the resulting experience. Anxiety, for example, in this paradigm is described as unpleasant because it involves the bubbling up of low-level prediction errors causing “attention pinches” across your experience, and thus disturbing the free-flow of energy that would exist in a homogeneous field. Prediction errors are not inherently unpleasant; they are unpleasant only to the extent that they cause asymmetries in your field of awareness!
Frank Yang also says that his big awakening felt like a “quantum jump”. It makes sense that a strong anti-fragile attractor for a new network topology would be self-reinforcing (a new lowest-energy state, metaphorically speaking, perhaps akin to a false vacuum collapse inside one’s mind!). Again, this is all very compatible with valence structuralism, if not STV.
Roger said that he will have to think about all of this. In the meantime, he shared with me some (amazing!) pictures he made to illustrate how his field of awareness has been transformed with meditation over time. Like Frank Yang, he identifies several discrete phase transitions. These are: (a) standard perception, (b) The Witness, (c) Big Mind, (d) No Self, and finally (e) No Self & Centreless Awareness (4th path!):
[…time…]
Roger:
[uploads this video – Jhanas 1-9 Experienced and Described In Real Time]
[…time…]
Roger:
Considering more what you said about impedance matching and adding resonance to experience:
Perhaps this is merely an analogy, but still: consider the tautness of a spider’s web. If a fly lands on it, at one part, the whole web will shake and the energy will transfer throughout in such a way that the spider can locate where on the web the fly landed. If the web is too taut then the energy of the fly landing won’t dissipate far enough for the spider to receive the information. However, if the web is too slack the fly could just break the structure of the web.
It might be interesting to consider why spiders build webs with a centre point and not as a straight or criss-crossing lattice.
So to relate this to consciousness and metabolizing stress… I would say my consciousness now feels like it’s more taut and lattice-woven rather than spider web-shaped with a middle [emphasis mine]. So this means when a stress point is activated somewhere in the experiential space, its energy doesn’t ripple as far out as it would have before, thus not being as disruptive.
And if we aliken the spider on the web to the epistemic agent, if he is situated on one spot and for all goings-on on the web to be known their information must travel to him, then the web must be not too taut so that all the ripples can reach him and he knows what’s going on. The problem with this set-up is that it means that knowing requires instability.
However, if we do away with the spider (a single point considered the epistemic agent) and make it so that the knowledge is attributed to the web itself, then the web can afford to be much more taut/less shaky/more robust, causing less negative valence.
So in some way I could say my experience (centerless consciousness) is more taut in this way, but this tautness doesn’t feel rigid or stiff, but rather very airy.
Indra’s net can have too much slack in it, if it’s not sewn together tightly and uniformly.
Pre-Awakening: The mind uses a fictitious “self-as-epistemic-agent” in a field of awareness that has slack and vibrates in unpleasant ways in the process of integrating information. The field of awareness relies on a network topology that is suboptimal for efficient stress dissipation.
Post-Awakening: The mind lacks any kind of center or self-as-epistemic-agent. The field of awareness is tout and extremely efficient at stress dissipation. The network topology has permanently changed to a far more symmetrical and regular configuration.
[…time…]
Roger:
Roger talks with Brendan Graham Dempsey: watch video here. He explains in more detail the spider web metaphor at 34:44.
[…and then in an email later…]
Roger:
Just for interest’s sake, and I don’t know if this bears any significance, but I’m ambidextrous by the way.
I know symmetry plays a major role in your hypotheses of valence and such.
In some way, I have thought that not having such a prioritization and weightiness to just one side of the body has balanced out my experience and perception (perhaps more than others), I’m not sure.
R
(As of the 23rd of November 2021, Roger states that he continues to be in the blissful state of centreless consciousness)
This conversation (and further exchanges I may share in the future) has reinvigorated my quest to describe states (and transformations) of consciousness in terms of changes to the network topology that underlies our field of awareness. Enlightenment might be described in “mystical” ways, but this could be simply due to lack of an adequate formal conceptual framework to make sense of it. But perhaps STV, impedance matching, and efficient stress dissipation through radical network topology reorganization without compromising self-epistemics could take us much further than before in this quest.
Also, if Roger was able to achieve these transformations at the tender age of 26, what is stopping the rest of us from doing the same?
Perhaps, what Marcin Kowrygo says is true: “Techno-boosted Arhatship: The rest is commentary”. (See also this fun story about enlightenment in Slate Star Codex).
If I were to add one thing to the wish-list, I’d say (in unison with people like Nick Cammarata and David Pearce): if we could have access to MDMA-like states of emotional wellbeing and empathy on tap, that would be fantastic (for many reasons). Plus, non-addictive real pain relief might very well be right behind the corner. So to revise our (admittedly cartoonish and partial) wish-list for the medium-term future of sentience: “MDMA-like emotional palette, non-addictive pain relief, and physiological Arhatship: The rest is commentary”. See you there, my friends!
Happy Thanksgiving Everyone (including the Turkeys, of course)!